© 2025 AI Questions. All rights reserved.
How Does AI Detection Work?
Answer
Generated by Ask AI Questions
AI Summary
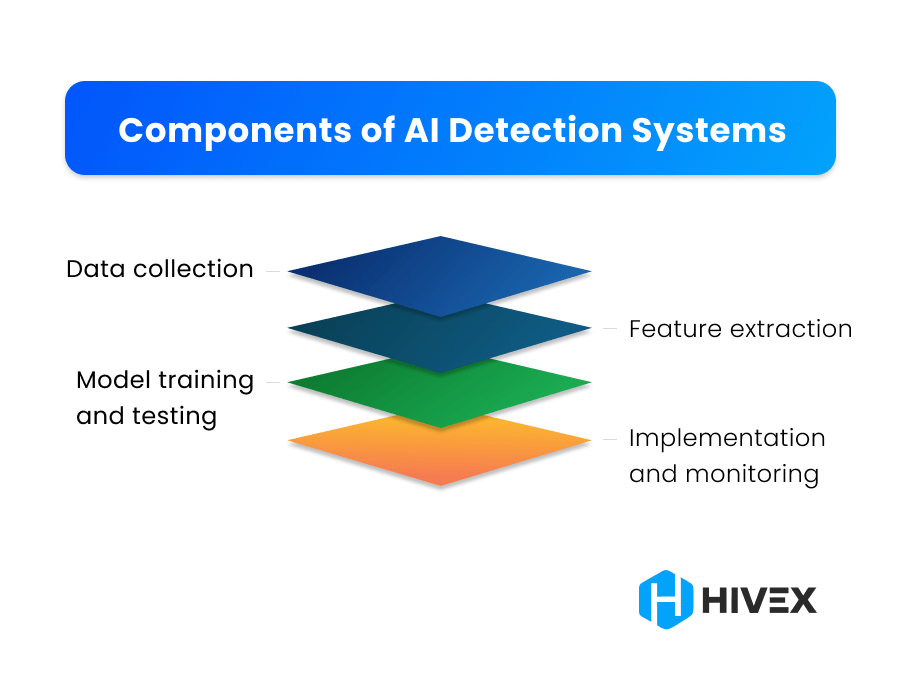
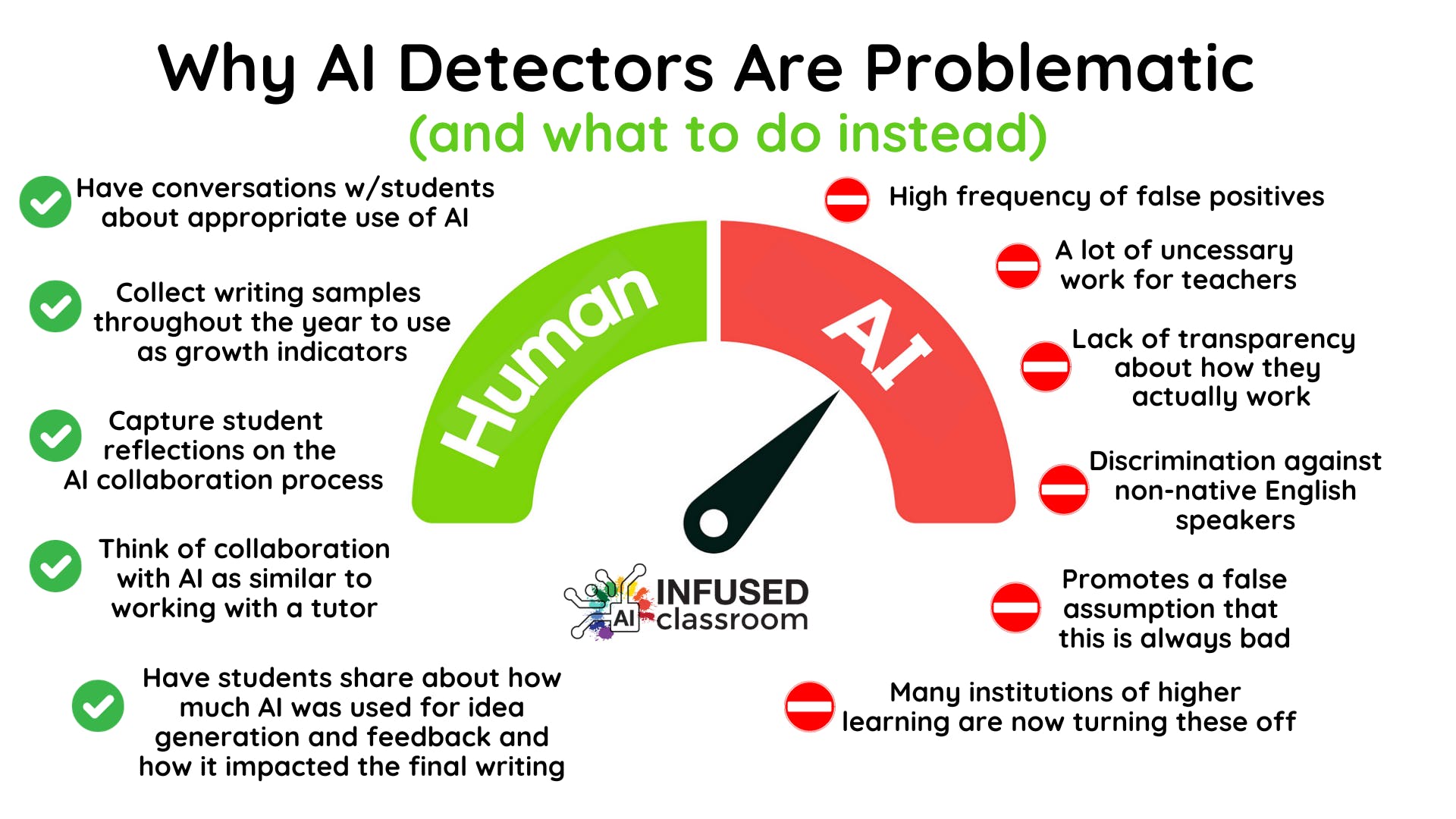
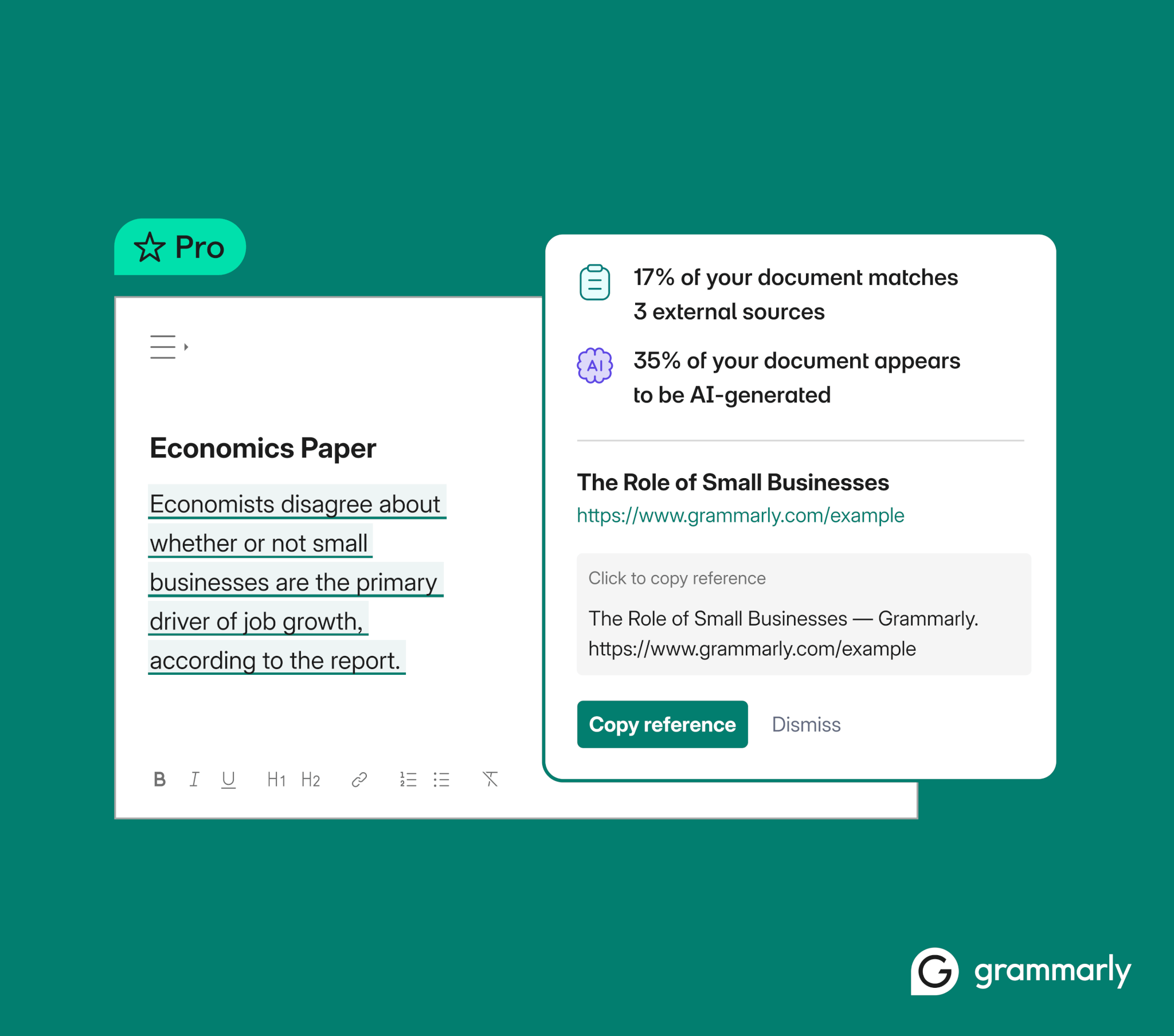
AI detection works by using machine learning models that analyze text features to decide if it is written by a human or an AI. These detectors break down the text into smaller parts called tokens, then examine patterns in word usage, sentence structure, and complexity. They measure "perplexity," which is how predictable the text is, and "burstiness," or variation in sentence length. AI-generated text tends to have low perplexity and uniform sentence patterns, while human writing is usually more varied and less predictable. The models are trained on large datasets labeled as either human- or AI-written and learn to recognize differences between them. After analyzing the text, the detector produces a probability score indicating how likely it was generated by AI. Although effective, AI detectors are not perfect and work best when combined with other checks because advanced AI can sometimes mimic human unpredictability.
Researched content
Ask Follow-Up Questions
Google Search Results
for "how does ai detection work"
.webp)